What to expect in this article
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a UCITS fund that tracks an
index like the
FTSE 100 or
EURO STOXX 50 and trades like a share. An ETF combines the benefits of a fund and a share in one security.
How do ETFs work?
ETFs enable you to invest cost-effectively in entire markets with one security. For example, with a single
MSCI World ETF, you spread your investment over around 1,600 companies from all over the world. In addition to equities, you can also invest in many other
asset classes with ETFs. Owing to this variety, ETFs are the perfect building blocks for private financial investments. ETFs simply copy a market index one-to-one and can be traded at any time on the stock exchange like a share.
justETF tip: ETFs offer numerous advantages: they are cost-effective, safe, transparent, widely diversified, flexible and liquid. Read more about the
advantages of ETFs here.
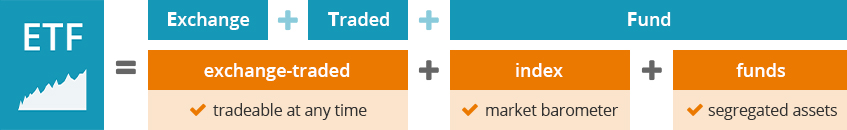
An ETF is an exchange-traded fund that tracks an index
The mode of operation and the advantages of an ETF can be best explained on the basis of three parts, from which the term “exchange-traded index fund” is formed.
![An ETF is an exchange-traded fund that tracks an index]()
What is a fund?
An investment fund is a collection point for the investors capital.
To put it simply, thousands of investors pool their funds and give the order to a professional (fund manager), to invest the funds as profitably as possible and with wide diversification in the context of a specified investment strategy.
How an investment fund works
![How an investment fund works]()
The investment classes (e.g. shares,
bonds and
commodities) in which the fund manager may invest is determined in the investment strategy.
In an investment fund, the investors’ assets are segregated. Thus, the funds are held in trust by a depository bank and are legally separated from the assets of the investment company. Therefore, the investor’s capital is protected even in case of insolvency of the investment company.
The manager of a typical mutual fund has the task to achieve a higher return on investment than the respective benchmark. However, according to academics, only a very few
fund managers succeed in this in the long run (period of more than 3 years).
What is an index fund?
The provider of an index fund ensures that it represents the development of an index as accurately as possible. The investments of an index fund (constituents and weightage) are exactly specified by the index. Indices are market barometers, which make the performance or return of total markets determinable.
An index fund has the great advantage that you, as an investor, always know where you have invested. As the composition of the underlying index such as the EURO STOXX 50 is always known. The European stock index (EURO STOXX 50) includes the shares of the 50 largest stock corporations of the Eurozone, weighted according to their size (as measured by the free-float market capitalization).
What is an ETF - Explained simply with the example of EURO STOXX 50
No elaborate analyses are required for stock picking due to
index replication in the case of index funds/ETFs (in comparison to the active investment funds). For this reason, the
ETF provider receives only low annual fees for his service. ETFs are, therefore, also significantly cheaper than traditional mutual funds - and in most cases show better performance.
What does exchange-traded mean?
ETFs are traded on the stock exchange similar to shares. Thus, you can buy and sell ETFs at any time during trading hours. In comparison to this, typical mutual funds are traded only once a day via the investment company.
While high upfront loads generally incur for the mutual funds, only the order fees of the bank and a usually small bid and ask difference (spread) at the time of trading on the exchange are paid for the
trading of ETFs.
Why doesn't my bank advisor recommend ETFs?
ETFs are unpopular products within commission-oriented financial advisors and branch banks. The reason for that is that these advisors usually live off commissions paid to them by the respective fund providers for selling their financial products. However, these commissions do not exist for ETFs. That is why most investment advisors are not overly interested in introducing ETFs to you (independent fee-based advisors are the exception here).
Still, it does not change the fact that ETFs are an excellent way to take your finances into your own hands - especially if you are still a beginner when it comes to investing.